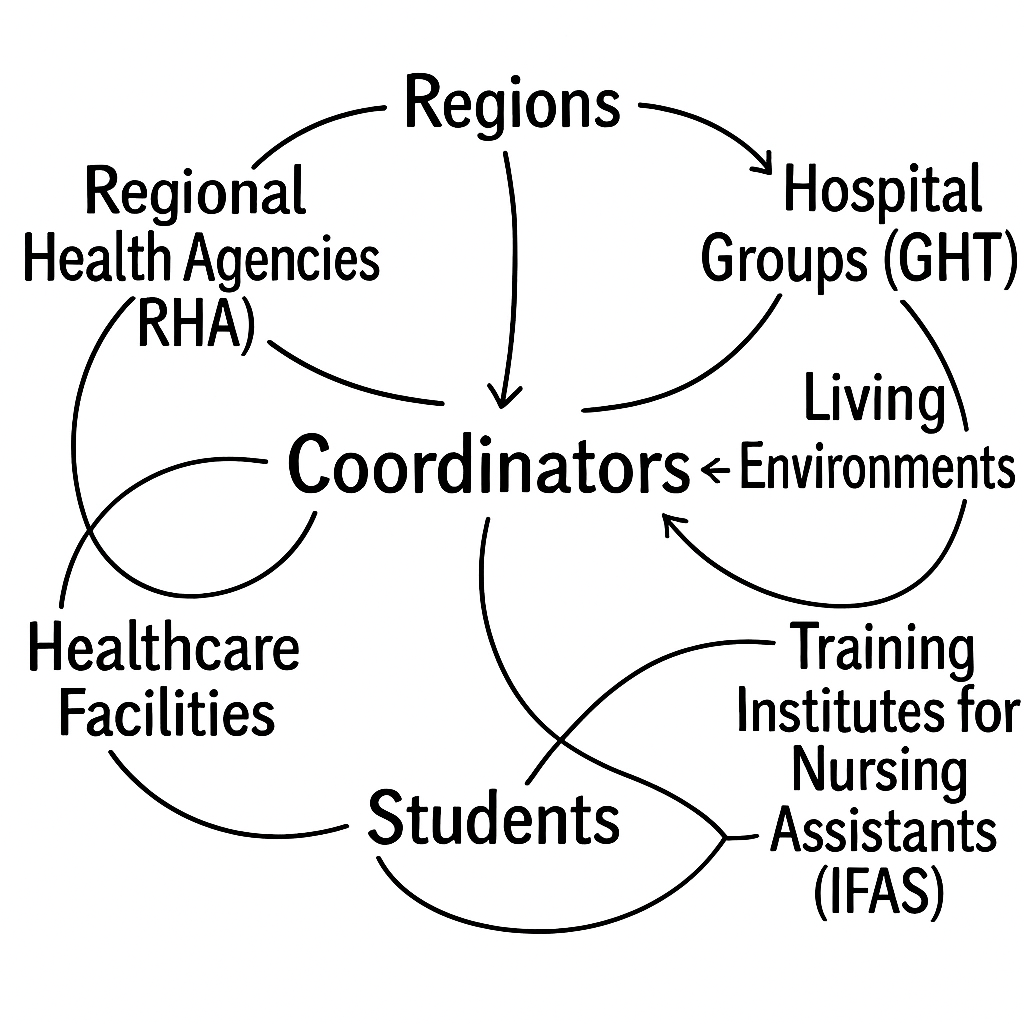
The importance of territorial coordination
The aim of territorial coordination of nursing placements is to strategically organize training sites to maximize students’ practical experience. This coordination involves not only the organization of placements, but also the distribution of students in different geographical areas to meet local needs. Such an approach makes it possible to :
- Ensure balanced coverage: By sending students to various regions, including rural areas and medical deserts, territorial coordination helps to ensure that these areas receive adequate support in terms of nursing staff.
- Promoting equity of access to care: Rural and disadvantaged areas often suffer from a shortage of healthcare personnel. By facilitating internships in these areas, students can fill these gaps and bring essential care to local populations.
- Building local capacity: Internships in these areas enable students to immerse themselves in local realities, better understand specific needs and adapt to the unique challenges of these regions.
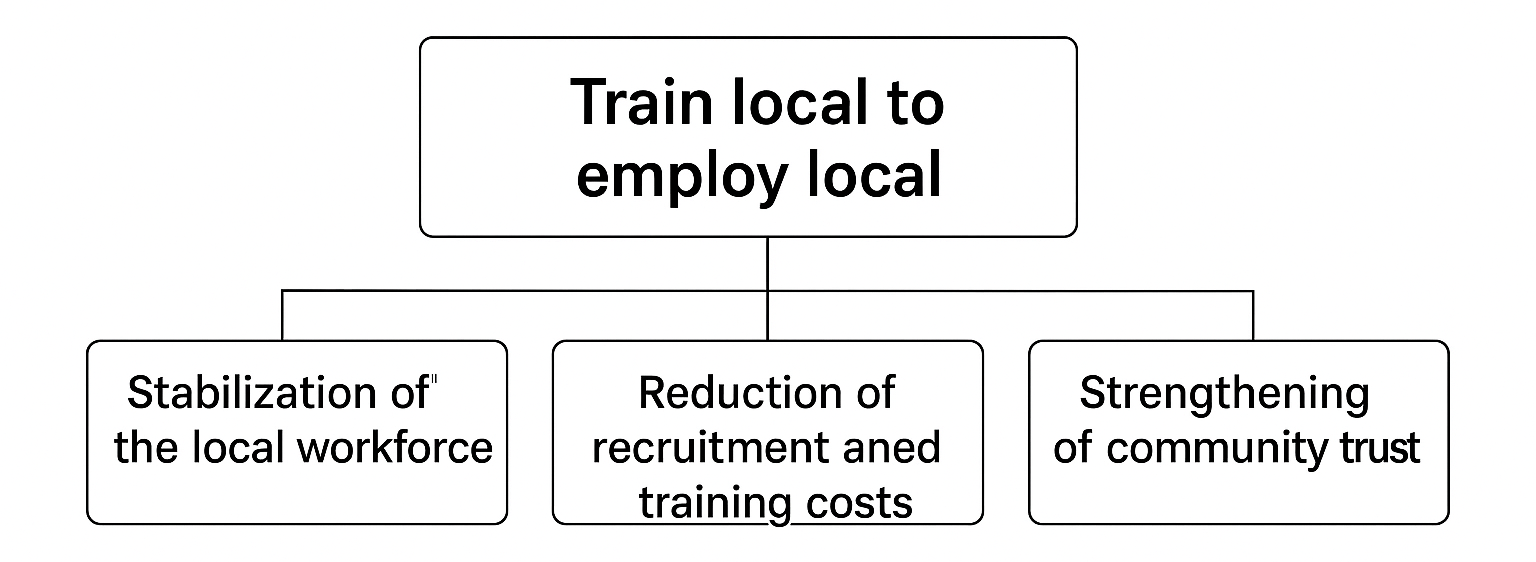
Train local, employ local
One of the most effective strategies for improving access to healthcare in rural and disadvantaged areas is to train local, employ local. This approach has several advantages:
- Stabilizing the local workforce: By training students from these regions, we increase the chances that they will choose to stay and work there after their training. This stabilizes and strengthens the local healthcare workforce.
- Reduced recruitment and training costs: Locally-trained students are already familiar with the particularities of their region, reducing the costs associated with adapting and training newcomers.
- Enhanced community confidence: Nurses from the local community are often better accepted and more empathetic towards patients, which improves the quality of care and strengthens patients’ trust in the healthcare system.
Case studies and success stories
To illustrate the positive impact of this coordination, let’s take a look at some successful initiatives:
- The regional internship program in Occitanie: This program has enabled nursing students to be effectively distributed throughout the region, including in rural areas. The results have shown a marked improvement in access to care and a reduction in health disparities.
- Local initiatives in Brittany: In Brittany, partnerships between IFSIs and local health establishments have made it possible to train and recruit nurses in traditionally under-resourced areas. Students trained locally have helped to stabilize the nursing workforce in these regions over the long term.
The challenges of territorial coordination
Despite its advantages, territorial coordination of nursing internships faces several challenges:
Logistics and funding: Organizing and funding placements in rural areas can be complex and costly. To overcome these obstacles, Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Marseille (AP-HM) has invested in a digital internship management platform, Interneo. This solution facilitates the management of internships, reduces logistical costs and improves the efficiency of coordination between the various players involved. Regional Health Agencies (ARS) and local authorities need to work together to provide the necessary resources and adopt similar digital tools to optimize internship management.
Attractiveness of rural areas: It can be difficult to convince students to choose placements in less attractive regions. It is therefore crucial to put in place incentives, such as financial aid or mentoring programs.
Quality of supervision: Ensuring quality mentoring in rural areas can be a challenge due to the lack of experienced professionals available to train students.

Reinforcing the humanization of care
The humanization of care is central to improving access to and quality of healthcare services. Sending student nurses to disadvantaged regions not only fills a gap, it also humanizes care in a number of ways:
- Empathy and understanding: Locally-trained nurses are often more empathetic and better able to understand the specific needs of their community.
- Continuity of care: The stable presence of nurses in a region enables better continuity of care, which is crucial for patient follow-up and chronic disease management.
- Development of trusting relationships: Nurses with a long-term presence can build trusting relationships with patients, improving quality of care and patient satisfaction.
Conclusion
In short, territorial coordination of nursing placements and the “train local, employ local” strategy play a crucial role in improving access to healthcare in rural and disadvantaged areas. By optimizing the distribution of qualified nurses and strengthening the local workforce, we can not only bridge the healthcare gap, but also humanize the care on offer. Overcoming logistical and financial challenges is essential to guarantee the success of these initiatives and ensure equitable healthcare coverage across all regions.



